English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
What are the most common challenges faced when using a stabilized soil mixing plant?
2024-09-30

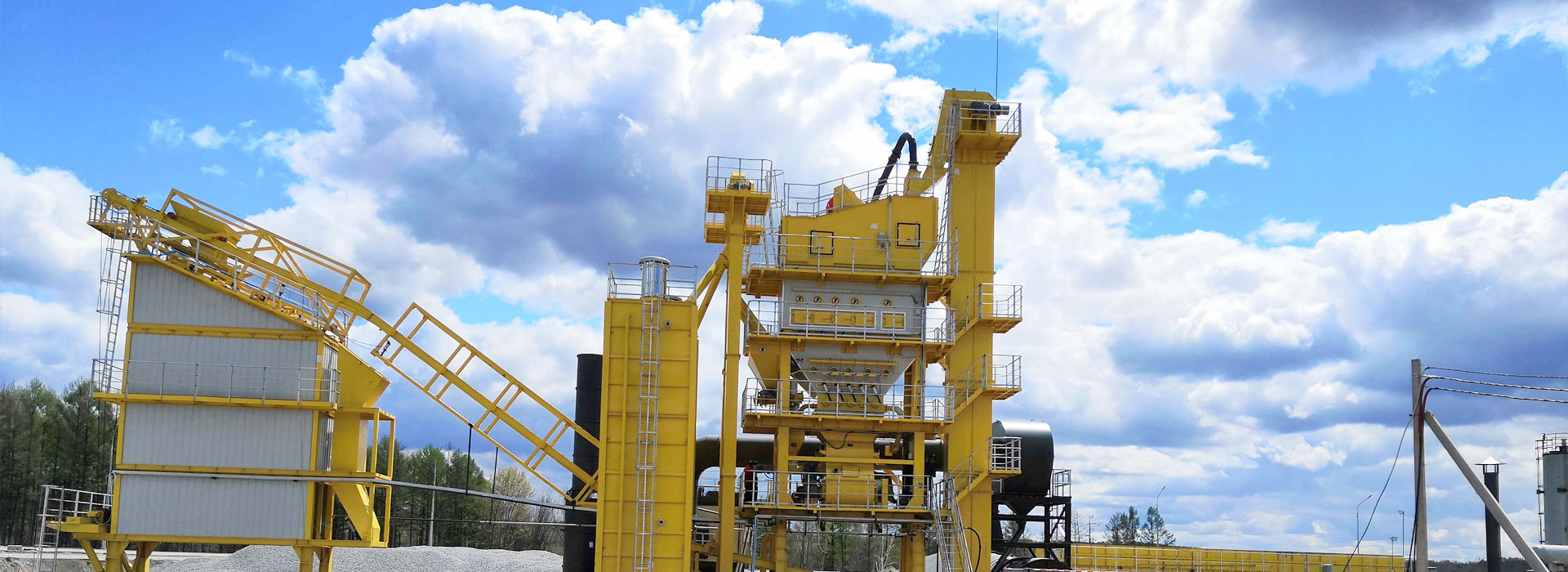
What are the most common challenges faced when using a stabilized soil mixing plant?
1. What are the different types of stabilized soil mixing plants?
2. What are the steps involved in the process of stabilized soil production?
3. What factors affect the quality of the final product?
Different types of stabilized soil mixing plants
There are different types of stabilized soil mixing plants that have been developed to suit different construction demands. These include:
Mobile Soil Mixing Plant: This is a portable plant that is easy to set up and move from site to site. It is ideal for small construction sites that require only a small amount of soil.
Stationary Soil Mixing Plant: This is a larger plant that is fixed on-site. It produces a larger quantity of soil and is suitable for larger construction sites.
Central-Mixed Soil Plant: This type of plant mixes all the materials at a central location, which ensures consistency in the final product.
The process of stabilized soil production
The production of stabilized soil involves the following steps:
Step 1: Preparation of materials
Soil, cement, and other materials are weighed and prepared according to the desired proportions.
Step 2: Mixing
The materials are mixed in a stabilized soil mixing plant. The mixing time is usually 2-3 minutes, and the result is a homogenous mixture.
Step 3: Storage
The finished product is stored in a silo or hopper before being transported to the construction site.
Factors affecting the quality of the final product
The quality of the final product is influenced by various factors, including:
Soil Type: Different soil types require different additives to achieve the desired results.
Moisture Content: The moisture content also affects the quality of the final product. The optimal moisture content should be between 10% and 18%.
Mixing Time: The mixing time affects the uniformity of the final product. The longer the mixing time, the more uniform the final product.
Additives: Different additives, such as cement and lime, have different effects on the final product. The proportion of these additives should be carefully calculated to achieve the desired results.
In conclusion, the stabilized soil mixing plant is an important production plant that is used in the construction industry to produce high-quality soil. To ensure the quality of the final product, it is important to consider factors such as soil type, moisture content, mixing time, and the use of additives.
At WUXI XUETAO GROUP CO., LTD, we specialize in the production of high-quality stabilized soil mixing plants. Our plants are designed to meet the demands of various construction projects and are known for their efficiency and reliability. For more information on our products and services, visit our website https://www.cxtcmasphaltplant.com or send an email to webmaster@wxxuetao.com.
List of 10 scientific papers on stabilized soil production
1. Gao, Y. et al. (2018). "Optimization of Mixing Parameters of Stabilized Soil Base in Highway Engineering." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 30(6): 06018016.
2. Wang, X. et al. (2017). "Influence of Aggregate Gradation and Cement Content on Properties of Stabilized Soil." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 29(12): 04017280.
3. Fang, X. et al. (2016). "Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Lime Stabilized Expansive Clay." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 28(1): 04015196.
4. Zhang, Q. and Yuan, J. (2015). "Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Soil Stabilized by Cement and Fly Ash." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 27(7): 04014268.
5. Pei, J. et al. (2014). "Research on the Compressive Strength of Stabilized Soil with Continuous Fiber." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 26(12): 04014068.
6. Wang, H. et al. (2013). "A Study on Dynamic Modulus of Stabilized Soil Using Resilient Modulus Test." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 25(8): 1040-1049.
7. Douglas, R. et al. (2012). "Characterization of Stabilized Soil Using X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 24(2): 227-236.
8. Li, X. et al. (2011). "Polypropylene Fiber Reinforced Soil Stabilization." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 23(12): 1728-1736.
9. Cui, Y. et al. (2010). "Effects of Curing Age and Temperature on the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Cement Stabilized Soil." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 22(9): 881-887.
10. Wu, S. et al. (2009). "Stabilization of Expansive Soil Using a Mixture of Cement and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag." Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 21(2): 76-85.