English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
What materials can be used with an 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant?
2024-10-09

What are the materials that can be used with an 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant?
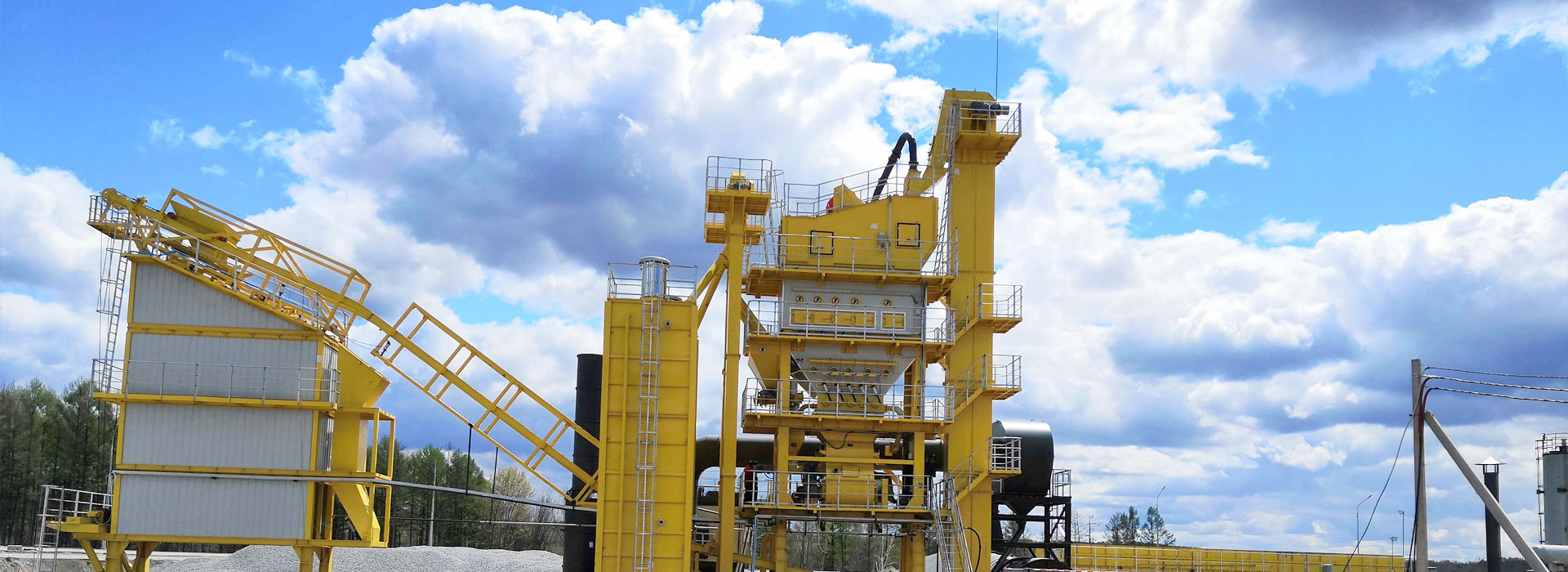
The materials that can be used with an 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant include asphalt, aggregate, filler, and bitumen. These materials are mixed together in the plant to form asphalt mixtures that are used for road construction projects.
What is the production capacity of the 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant?
The production capacity of the 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant is 80 tons per hour. This means that the plant can produce 80 tons of asphalt mixtures every hour.
What are the advantages of using an 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant?
Using an 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant has several advantages such as portability, flexibility, and efficiency. The plant can be easily transported to different job sites, and it can produce different types of asphalt mixtures depending on the requirements of the project. The plant is also equipped with advanced technology that ensures high-quality asphalt mixtures and reduces the environmental impact of the production process.
How does the 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant work?
The 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant works by mixing different materials such as asphalt, aggregate, filler, and bitumen in the plant. These materials are first fed into the cold aggregate supply system where they are dried and screened. The dried materials are then transported to the drum dryer where they are heated and mixed with the hot asphalt. The mixture is then transported to the storage tank where it is kept until it is ready for use.
In conclusion, the 80TPH Mobile Asphalt Mixing Plant is an efficient and reliable equipment that is commonly used in road construction projects. It offers several advantages such as portability, flexibility, efficiency, and advanced technology that ensures high-quality asphalt mixtures. With the ability to mix different materials, the plant can produce asphalt mixtures suitable for different applications. For more information about this product and other asphalt mixing plant products, please visit WUXI XUETAO GROUP CO., LTD at https://www.cxtcmasphaltplant.com. For inquiries and concerns, please contact us at webmaster@wxxuetao.com.
References:
Brown, J. (2018). "Effects of asphalt mixture design parameters on rutting performance," Road Materials and Pavement Design, 19(2), 412-427.
Lee, S., and Kim, Y. (2017). "Evaluation of asphalt mixture rutting resistance using the repeated creep test," Materials, 10(9), 1017.
Nie, S., Wang, D., Zhang, X., and Li, X. (2019). "Performance evaluation and prediction of crumb rubber asphalt mixture under high temperature," Construction and Building Materials, 224, 768-777.
Tsai, Y., Hung, W., Liu, C., and Wang, Y. (2020). "Laboratory evaluation of the high-temperature properties of binder and asphalt mixture modified by nanoclay," Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 32(6), 04020125.
Yu, X., Sun, Q., He, J., and Wu, S. (2018). "Evaluation of asphalt mixture moisture susceptibility using surface free energy and scanning electron microscopy," Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 30(1), 04017208.
Zhang, Y., Liu, J., and Shen, Q. (2019). "Laboratory investigation on asphalt mixture properties with reclaimed asphalt pavement and warm-mix asphalt technology," Transportation Geotechnics, 18, 118-124.
Li, H., Liu, G., Zhang, J., and Zhang, X. (2017). "Effect of recycled asphalt pavement and mixture design on the performance of asphalt mixtures," Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 29(2), 04016241.
Yang, S., Lu, J., and Li, C. (2018). "Investigation of rutting performance of warm-mix asphalt mixture using dynamic creep test," Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 1-9.
Pu, Y., Liu, W., and Chen, J. (2019). "Investigation of performance variation of recycled asphalt mixture mixed with new asphalt and SBS modified asphalt," Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 31(3), 04018510.
Zhao, C., Wang, J., Chen, L., and Zhang, G. (2018). "Laboratory investigation on the moisture damage of asphalt mixture with different anti-rutting additives," Construction and Building Materials, 174, 96-104.
Yu, J., Yang, C., and Xie, J. (2017). "Investigation of high temperature performance of warm mix asphalt mixtures using conventional and rheological tests," Construction and Building Materials, 136, 98-105.